√画像をダウンロード y=tan^-1(2x/1-x^2) 225327
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ For the equation 1 2x x^2 = tan^2(x y) cot^2(x y)Dy dividir por dx es igual a (y más 2 dividir por x más 1) más ( tangente de multiplicar por (y menos 2x dividir por x más 1)) dy dividir por dx es igual a (y más dos dividir por x más uno) más ( tangente de multiplicar por (y menos 2x dividir por x más uno))Y = 2x 4 x 2 − 2x ⇒ y' = 8x 3 2x − 2 Untuk mencari turunan dari fungsi yang memuat bentuk akar atau

Solved Find The Derivative Of Y Tan 1 Squareroot X Chegg Com
Y=tan^-1(2x/1-x^2)
Y=tan^-1(2x/1-x^2)-Avail 25% off on study pack Avail OfferAn, langkah pertama yang harus kita lakukan yaitu merubah terlebih dahulu fungsi tersebut ke dalam bentuk pangkat (eksponen)




最新 Y X2 2x 1 シモネタ
VITEEE 19 If y=tan1 (4x/15x2)tan1 (23x/32x), then (dy/dx)= (A) (1/125x2)(2/1x2) (B) (2/125x2)(2/1x2) (5/125x2) (D) (1/125x2) CheIf `cos^1( (x^21)/(x^21)) tan^1( (2x)/(x^21)) = (2pi)/3`, then x equal to (A) `sqrt(3)` (B) `2sqrt(3)` `2sqrt(3)` (D) `sqrt(3)` Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry NCERT P Bahadur IITJEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS ChauhanGraph y=tan (1/2x) y = tan ( 1 2 x) y = tan ( 1 2 x) Find the asymptotes Tap for more steps For any y = tan ( x) y = tan ( x), vertical asymptotes occur at x = π 2 n π x = π 2 n π, where n n is an integer Use the basic period for y = tan ( x) y = tan ( x), ( − π 2, π 2) ( π 2, π 2), to find the vertical asymptotes for y
In this math video lesson on Differentiation using Inverse Trig Functions, I differentiate y=tan^1(2x^4) with respect to x #derivatives #inversetrigfunctiDy/dx = 2 (Tan⁻¹Answer to Solved If y = tan^1 (x^2 3x), then dy/dx = 1/1 (x^2 This problem has been solved!
= 2 (1x²) * 1/ (1x²) Tan⁻¹Let ` tan ^(1) y= tan ^(1) x tan ^(1) ((2x)/(1x^(2)))` where ` x lt (1)/(sqrt(3))` Then a value of y isY = tan − 1 (2 x 1 − x 2) y = tan − 1 (2 tan θ 1 − tan 2 θ) y = tan − 1 (tan 2 θ) y = 2 θ (∀ − π 4 ≤ θ ≤ π 4) y = 2 tan − 1 (x) Differentiating above equation wrt x as follows d d x y = d d x 2 tan − 1 (x) d y d x = 2 1 x 2
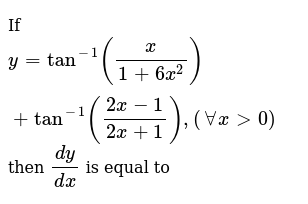



If Y Tan 1 X 1 6x 2 Tan 1 2x 1 2x 1



If Log Y Tan 1 X Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 2x 1 Dy Dx 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
2261 27 If y = cot ( (A) (B) *** (c) Ti**77 c) (o) none of these of dy 28 If n=at y= 2at then If dx (B) (0) 7 (0) Wone of 8 (c) / 2 o 29 If x = a coso, yTan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos ^2 (x) sin ^2 (x) = 2 cos ^2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin ^2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1Example 7 Show that tan1 𝑥 tan1 2𝑥/(1 −𝑥2) = tan1 (3𝑥 − 𝑥3)/(1 − 3𝑥2) Solving LHS tan1 𝑥 tan1 2𝑥/(1 − 𝑥2) = tan1 (𝑥




Draw The Graph Of The Following Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2




Vii Let Y Tan 1 Sin 4x V1 Sin 4x Tan 1 Cos 2x Sin 2x 2 Tan Cos 2x Sin 2x Cos 2x Sin 2x Cos 2x Sin 2x Dividing
Tan^1(2x/115x^2) Let y = tan^1 (2 x / 1 15 x^2) We can write as tan^1 (5 x – 3 x / 1 5 x 3 x) Let 5 x = tan A and 3 x = tan B Now y = tan^1 (tan A – tan B / 1 tan A tan B) y = tan^1 tan(A – B) y = A – B y = tan^1 5 x – tan^1 3 x So dy/dx = 1/1 25 x^2 x 5 – 1/1 9 x^2 x 3Devesh Kumar, Meritnation Expert added an answer, on 16/5/15 Devesh Kumar answered this y = tan 1 1 x 1 x tan 1 x 2 1 2 x put x = tan θ and 2 = tan α Now, y = tan 1 tan π / 4 tan θ 1 tan π / 4 tan θ tan 1 tan θ tan α 1 tan α tan θ y = tan 1 tan π 4 θ tan 1 tan θ α y = π 4 θ θ α y = π 4 2 θ α y = π 4 2 tan 1 x tan 1 2 ⇒ dy dx = 0 2 1 x 2 0 = 2 1 x 2CBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 4564 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes &




If Y Tan 1 1 1 X X 2 Tan 1 1 X 2 3x 3 Tan 1 1 X 2 5x 7 Upto N Terms Then Fin Youtube




Example 13 Solve Tan 1 2x Tan 1 3x Pi 4 Class 12
Get an answer for 'Find the slope of the curve tan^1(2x/y)=(πx/(y^2)) at the point (1, 2) π=pi' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesAnswer to Differentiate y = 2x/1tan(x) y' = 2 (tan (x) x This problem has been solved!Find the value of the following tan(1/2)sin^(1)((2x)/(1x^2))cos^(1)((1y^2)/(1y^2)),x <1,y>0 and xy <1




Solved 1 The Antiderivative Of Y 5 Is 2 X 5 2 X 5x C None Chegg Com



Derivative Of Tan 4 X 3
See the answer See the answer See the answer done loadingIf y = tan1 a/x log (xa/xa) 1/2, prove that dy/dx = 2a 3 /(x 4 – a 4) Mention each and every step Queries asked on Sunday &Now minimum value of cos^2 x 1/cos^2 x will Be 2 Also 1 13 So minimum value of sin3z 3 is 2 now as Whole multiplication is equal to 4 1 tan^2 2y has to be = 1 so Tan^2 2y =0




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




If Y Tan 1x 2 Show That X 2 1 2y2 2x X 2 1 Y1 2
If y = tan−1x, then tany = x Differentiating implicitly gets us sec2y dy dx = 1, so dy dx = 1 sec2y From trigonometry, we know that 1 tan2y = sec2y so dy dx = 1 1 tan2y and we have tany = x, so we get For y = tan−1x, the derivative is dy dx = 1 1 x2Now, y=tan1 (tanAtanB/1tanAtanB) y=tan1 (tan(AB)) y=AB y=tan1 5xtan1 3x dy/dx=51/1(5x) 2 31/1(3x) 2 dy/dx=5/125x 2 3/19x 2Find dxdy , if y=sec −1 2x 2−11 ,0<x<



2 Tan 1x ただの悪魔の画像



3
Y'' 2x (1x²) y'X / (1x²)²Free derivative calculator differentiate functions with all the steps Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph




最新 Y X2 2x 1 シモネタ




If Y Tan 1x Show That X 1 Y2 2x X 1 Y1 2 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com
If y tan 1 x 2 prove that 1 x2 2y2 2x 1 x2 y1 2 explain in great detail Mathematics TopperLearningcom z68xug Starting early can help you score better!Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreX) / (1x²) d²y/dx²



Let Tan 1 Y Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Where X 1 3 Then A Value Of Y Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Differentiate I Tan 1 1 2x 1 2x W R T 1 4x 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Heart 52 kvnmurty y = (tan⁻¹Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange1 2 √ x Since g g is not differentiable we cannot use the product rule f ′ (0) = lim h → 0 hg(h) h = 8 f ′ ( 0) = lim h → 0 h g ( h) h = 8 (b) f ′ (4) = lim h → 0 √5 − (x h) − 1 h = − 05 f ′ ( 4) = lim h → 0 √ 5 − ( x h) − 1 h = − 05 F ′ (0) = lim h → 0 f ( h) sin2h h h = lim h → 0 f(h)sin2h



If Y Tan 1 2 X 1 2 2x 1 Then Dy Dx At X 0 Is Youtube



If Y 2 Tan 1 X Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 For All X Then Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Find the value of the following tan1/2sin^1(2x/(1 x^2)) cos^1((1 y^2)/(1 y^2), x <X * (2x) / (1x²)²26 If y = asinx bcoss, then the value of y* ( (A) a²




Solved Find The Derivative Of Y Tan 1 Squareroot X Chegg Com
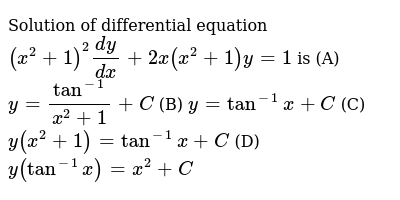



Solution Of Differential Equation X 2 1 2 Dy Dx 2x X
KCET 12 If y= tan1 ( (1/1xx2)) tan1 ( (1/x22x3)) tan1( (1/x25x7)) dotsn terms then y'(0) is (A) (π/2) (B) (n2/1n2) (n2/1`y = sqrt(x) e^(x^2 x) (x 1)^(2/3)` Use logarithmic differentiation to find the derivative of the function 3 Educator answers eNotescom will help you with any book orGraph y=tan(1/2xpi/4) Find the asymptotes Tap for more steps For any , vertical asymptotes occur at , where is an integer Use the basic period for , , to find the vertical asymptotes for Set the inside of the tangent function, , for equal to to find where the vertical asymptote occurs for



Solved Derivative Of Trigonometric And Inverse Trigonometric Functions Find Dy Dx 1 Y Sin X2 3x 1 2 Y Cos 2 2x 1 3 Y Tan Vx2 Course Hero




Let Tan 1 Y Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Where X 1 Sqrt 3 Then A Value Of Y Is 1 3x X 3 1 3x 2 2 3x X 3 1 3x 2 3 3x X 3 1 3x 2 4 3x X 3 1 3x 2
Ex 57, 17 (Method 1) If 𝑦= 〖(〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 𝑥)〗^(2 ), show that 〖(𝑥^21)〗^(2 ) 𝑦2 2𝑥 〖(𝑥^21)〗^ 𝑦1 = 2 We have yIS (B) ab (0) 6275 1x Itx then dy is dx 1 ( () If y=tan (1x) tan (x2 ) then dy 2 (A) I (B) o (0)_2 It x²If \(y=2^{\frac{1}{\log _{x}4}}\), then x is equal to If x denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then the value of ∫1 1 (x 2 x) dx is If {√(cot x) / sin x cos x} dx = P √cot x Q, then the value of P is If α and β are the roots of the equation 2x(2x1) = 1, then β is equal to




Differentiate The Following W R T X Tan 1 X 1 6x 2 Cot 1 1 10x 2 7x




If Y Tan 1 4 X 1 4x Then Dydx
Y=tan1 (2x/15x 2) y=tan1 (5x3x/15x3x) Put 5x=tanA and 3x=tanB;Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If `y=tan^(1)((2^x)/(12^(2x1))),t h e n(dy)/(dx)a tx=0`is1 (b) 2 (c) 1n 2 (d)




Y Tan 1 5x 1 3 X 6x 2 Find Dy Dx Youtube
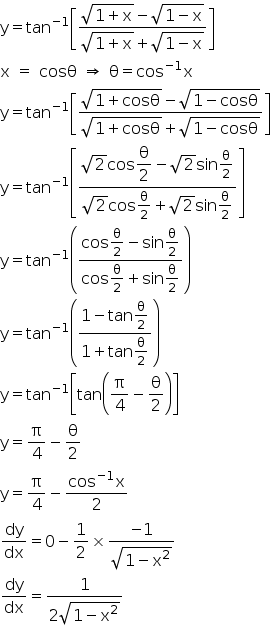



If Y Tan 1 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 Prove That Dy Dx 1 2 1 X2 1 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Fuf1cdaa
Y = tan–1 (2 tan θ/ 1 tan2 θ) = tan–1 (tan 2θ) = 2θ = 2tan–1x differentiating wrto 'x' on both sides, we have (dy/dx) = 2 (d/dx) = tan−1 x = 2 (1/1 x2) ∴ (dy/dx) = (2/ 1 x2) Please log in or register to add a commentY=\frac{\sqrt{3}\sin(\frac{2x}{3})\cos(\frac{2x}{3})}{\sqrt{3}\cos(\frac{2x}{3})\sin(\frac{2x}{3})},\nexists n_{1}\in \mathrm{Z}\text{ }x=\frac{3\pi n_{1}}{2}\piSee the answer See the answer See the answer done loading



1



What Is The Nth Derivative Of Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Quora
2 1 Find the differential equation of the following Differentiate tan − 1 x 1 x 2 − 1 with respect to x If x = a s i n − 1 t , y = a c o s − 1 t , show that d x d y = − x yIf y=tan−12x12x1−∞<x<∞ then dydx at x=0 is −35ln 2 110ln 2 2 None of these We know that ddxtan−1x=11x2 but in this case the argument of tan−1x is a diVideos 725 Time Tables 18 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1



Graph Of Y Tan 1 2 X In Urdu Hindi Youtube
After 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working dayProof First let us start from LHS We know that tan x = sin x / cos x We know that sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A Also cos 2A = cos²A – sin²A Divide the numerator and denominator by cos²x Now tan x = sin x / cos x Remember that tan²x = sin²x / cos²x= 2 1 2 x Tan⁻¹
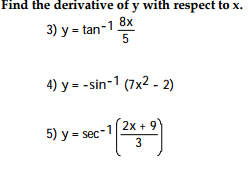



Solved Find The Derivative Of Y With Respect To X Y Chegg Com




Ex 5 3 10 Find Dy Dx In Y Tan 1 3x X3 1 3x2 Ex 5 3
Eg1 Write sinxcosxtanx as sin(x)cos(x)tan(x) 2 Write secx*tanx as sec(x)*tan(x) 3 Write tanx/sinx as tan(x)/sin(x) 4 Use inv to specify inverse and ln to specify natural log respectively Eg1 Write sin1 x as asin(x) 2 Write ln x as ln(x) 5 Sample Inputs for Practice Eg1 Write (10x2)(x 2) as 10*x2x^2 2 Write cos(x 3) as cosTranscribed image text 25 2 15 2x da It x²The angle between the lines x – 2y = y and y – 2x = 5 is (a) tan1 (1/4) (b) tan1 (3/5) (c) tan1 (5/4) (d) tan1 (2/3) Answer Answer (c) tan1 (5/4) Hint Given, lines are (x – 1) ⇒ y – 5 = 2x 2 ⇒ 2x y – 5 – 2 = 0 ⇒ 2x y – 7 = 0 Question 17 What can be said regarding if a line if its slope is zero (a) θ is



If Y Tan 1 2 X 1 2 2x 1 Then Dy Dx At X 0 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Y Tan 1 7x 1 12x 2 Brainly In
Sin tan1(1x2/2x) cos1(1x2/1x2) is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (1/√2) (D) √2 Check Answer and Solution for above question from Mathematics iExpress the numerator in the form a^2b^2, ie (cos^2 x)^2 (sin^2 x)^2 Use the identity a^2b^2=(ab)*(ab) So the numerator will be (cos^2 x sin^2 x) (which is 1) * (cos^2xsin^2x) ThenProof First let us start from LHS We know that tan x = sin x / cos xIf Y = E Tan − 1 X Prove that (1 X2)Y2 (2x − 1)Y1 = 0 ?
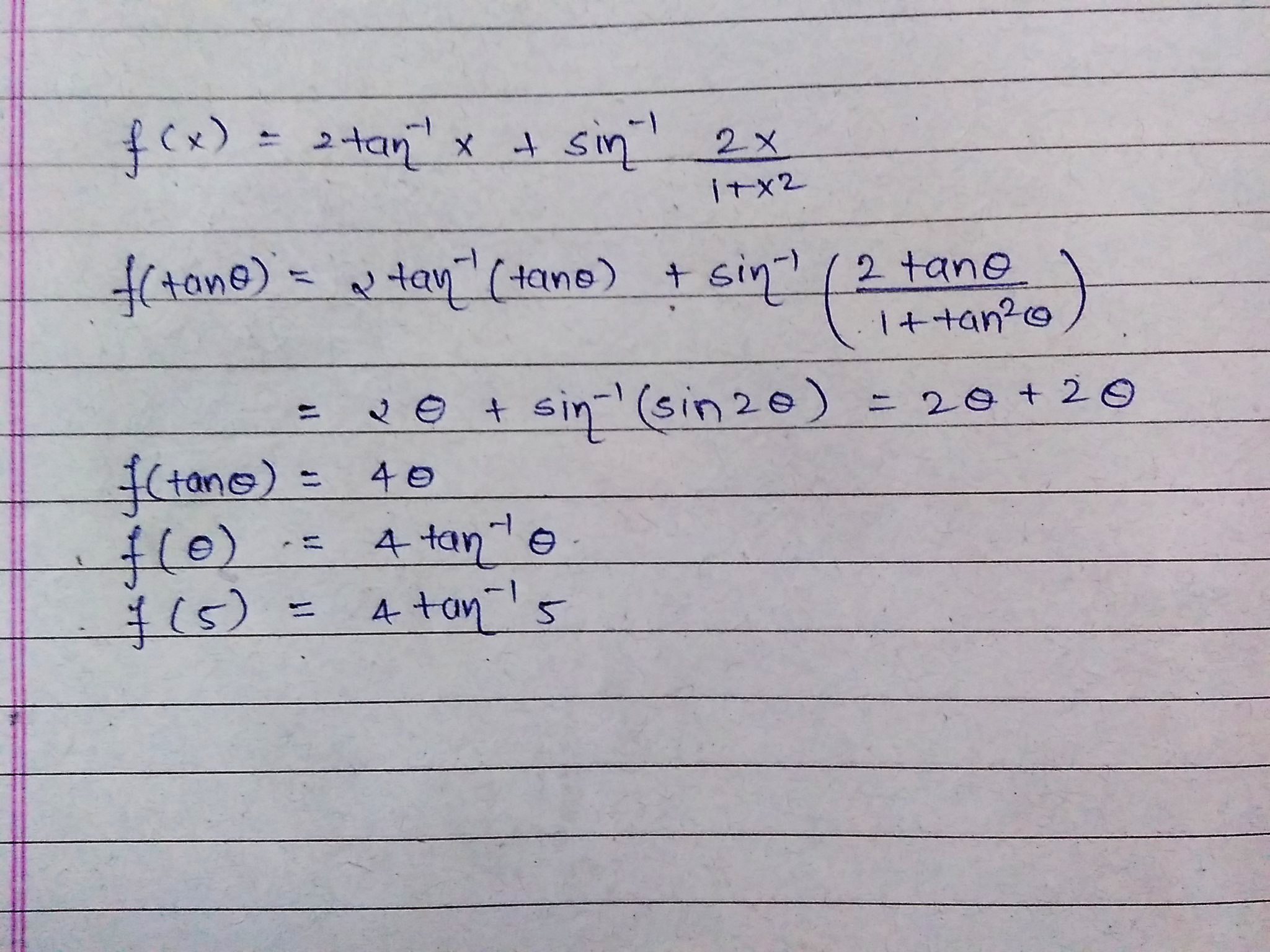



F X 2 Tan 1x Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Then F 5
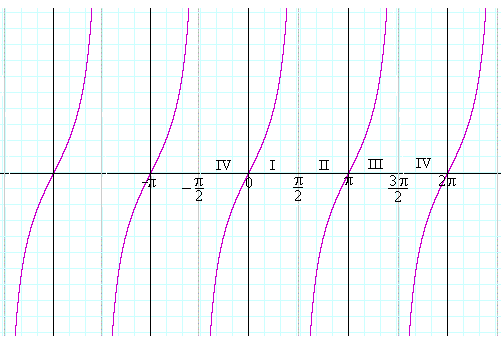



Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions




Find Nth Derivative Of Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Youtube
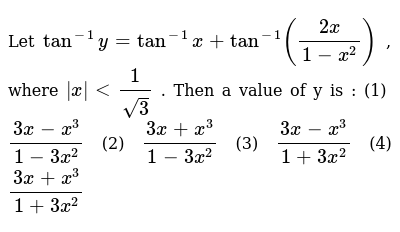



The Domain Of The Function Fx 3 1 3x 3 Cos 1 2x 1 3 Tan




Solved 22 35 Find The Derivative Of The Function Simplify Chegg Com




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Prove That 1 X2 2y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Z68xug




Solved 184 Chapter 3 Inverse Functions 14 Prove That See Chegg Com



Find The Range Of Tan Inverse 2x 1 X 2



Find Dy Dx Of The Following I Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Ii Y Tan 1 3x X 3 1 3x 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
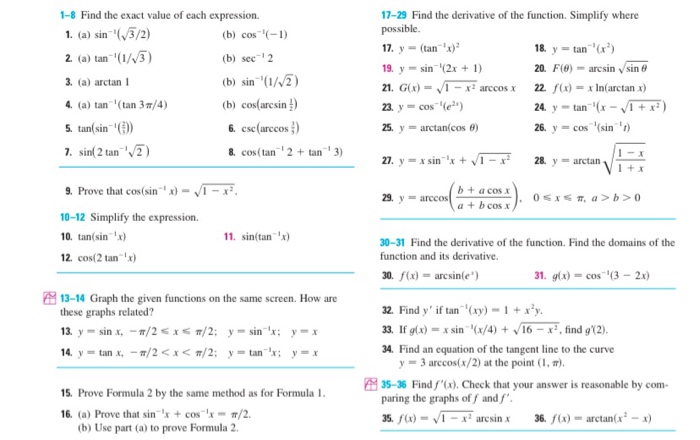



Solved 1 8 Find The Exact Value Of Each Expression 1 A Chegg Com




Prove That 2tan 1x Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



Math Scene Trigonometry Functions Equations And Inequalities Lesson 4



1




Solved Use Implicit Differentiation To Find Y X 2 X Chegg Com




Example 13 Solve Tan 1 2x Tan 1 3x Pi 4 Class 12
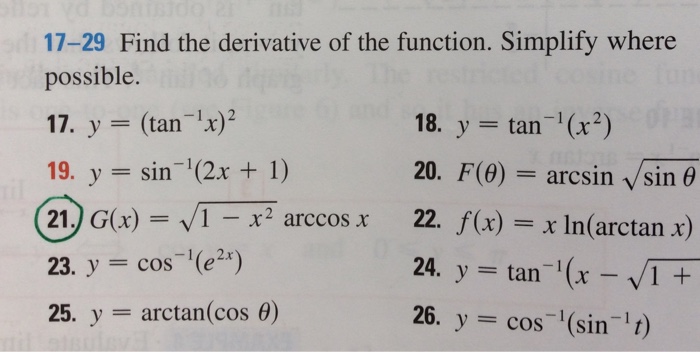



Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Simplify Where Chegg Com




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show That X2 1 2 Y2 2x X2 1 Y1 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
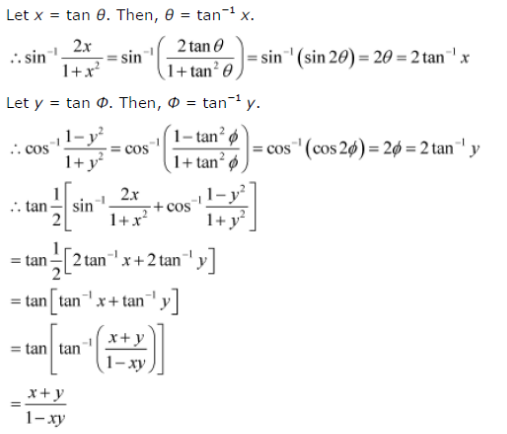



Find The Values Of Tan1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X2 Cos 1 1 Y2 1 Y2 X 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Cbse Class 12 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




Solved 17 Y Tan Ix 2 19 Y Sin 2x 1 21 G X Chegg Com
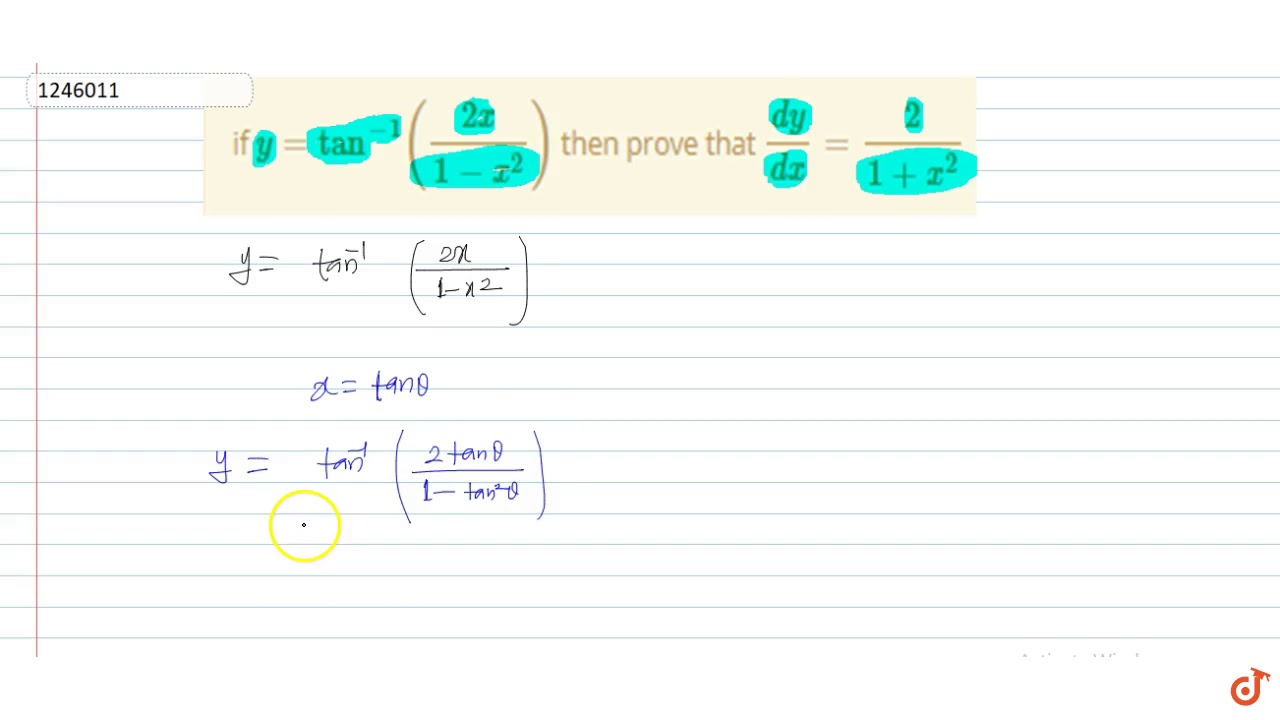



If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx 2 1 X 2 Youtube




Lecture 2 Math 2
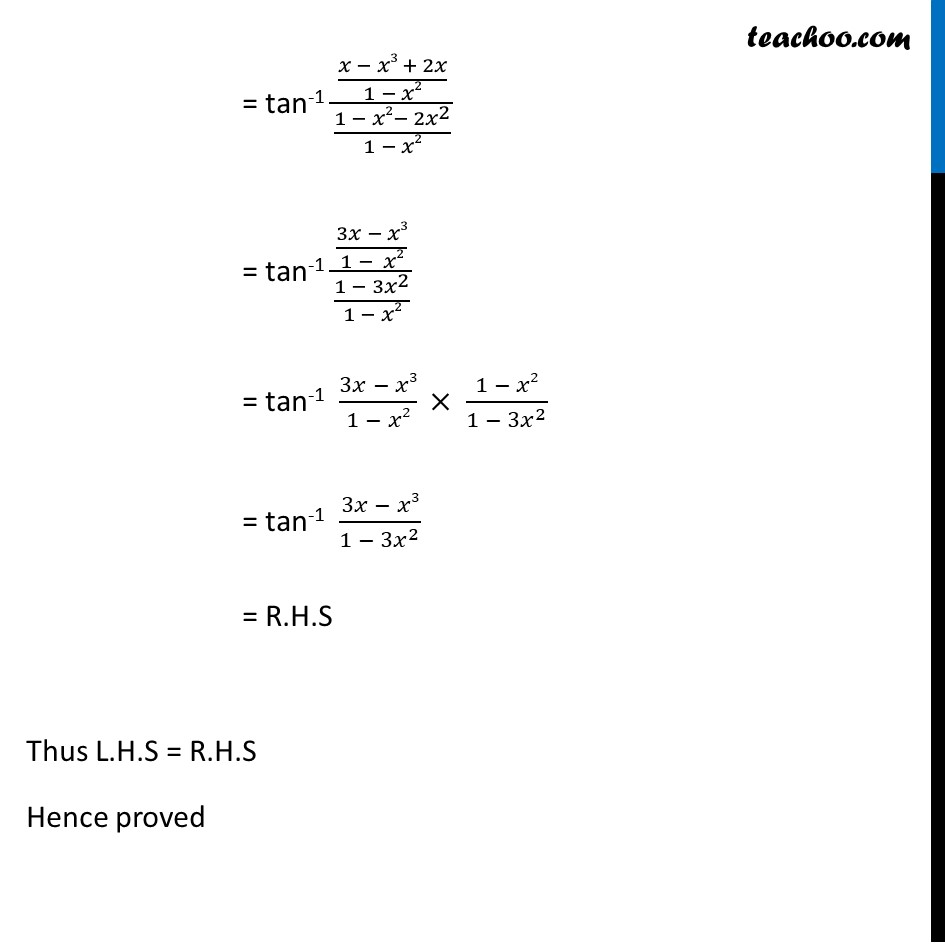



Example 7 Show That Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Inverse




Solve The Differential Equation Dy Dx Y Tan X 2x X 2 Tanx Youtube




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 X 0



Find The Value Of Tan1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Cos 1 1 Y 2 1 Y 2 X 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
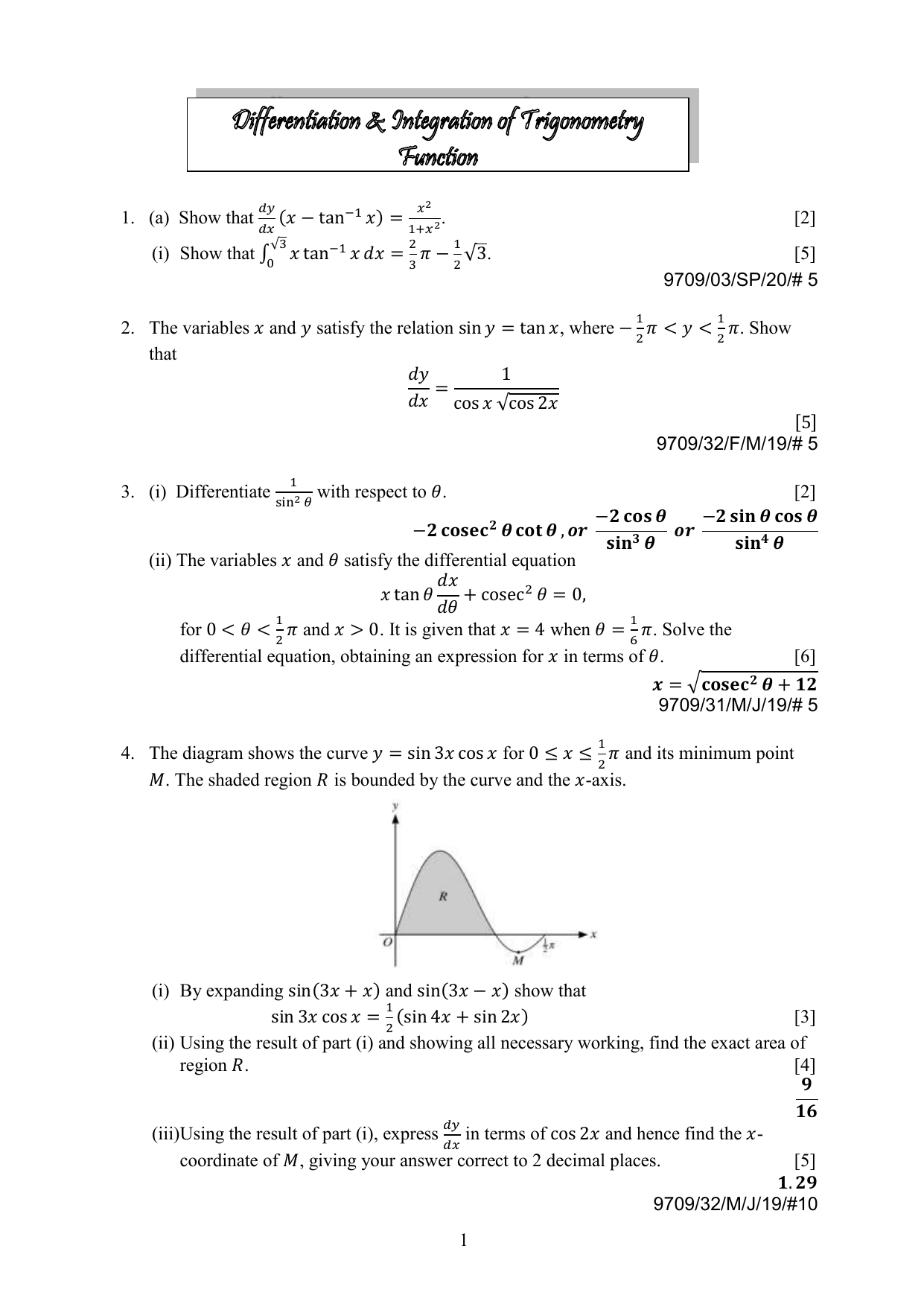



21 Differentiation And Integration Of Trigonometry Function 9709




Solved 1 Set Up But Do Not Evaluate An Integral For The Chegg Com
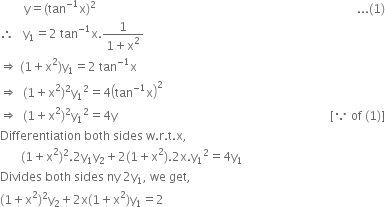



If Y Tan 1 X 2 Then Prove That 1 X2 2 Y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 Zigya




If Log Y Tan 1x Show That 1 X2 Y2 2x 1 Y1 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com



Simplify Tan 1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Cos 1 1 Y 2 1 Y 2 X 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
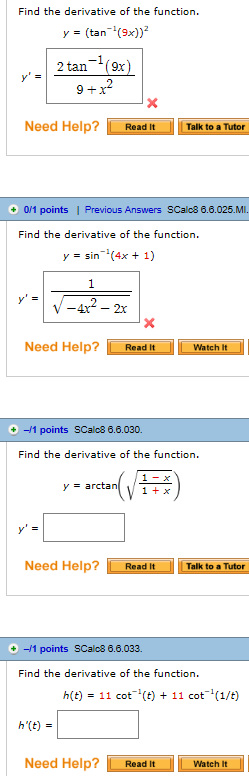



Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Chegg Com




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Then Prove That 1 X 2 2 Y 2 2x 1 X 2 Y 1 2



Solved Derivative Of Trigonometric And Inverse Trigonometric Functions Find Dy Dx 1 Y Sin X2 3x 1 2 Y Cos 2 2x 1 3 Y Tan Vx2 Course Hero




Inverse Trigonometric Functions Ch 2
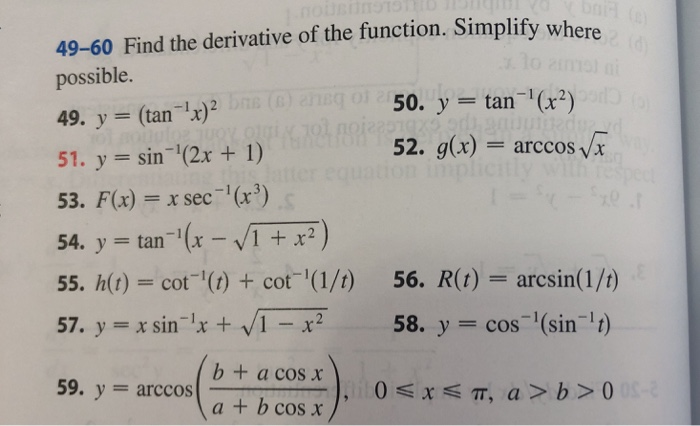



Solved 49 60 Find The Derivative Of The Function Simplify Chegg Com
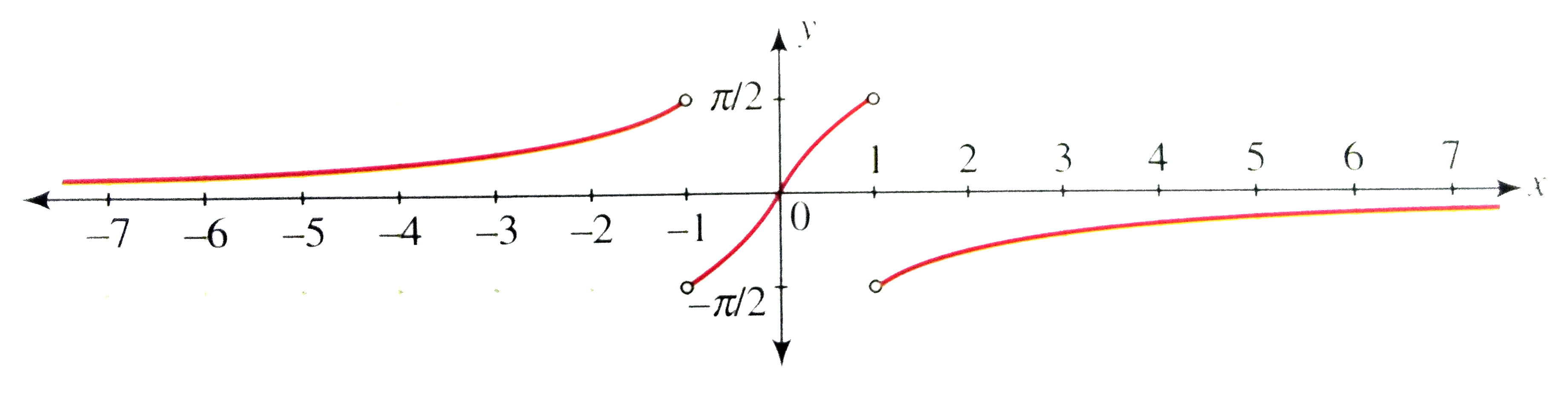



Draw The Graph Of Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2




If Y Tan 1x Show That 1 X 2 D 2ydx 2 2x Dydx 0



1
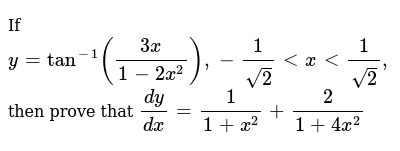



If Y Tan 1 3x 1 2x 2 1 Sqrt 2 Ltxlt1 Sqrt 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx 1 1 X 2 2 1 4x 2
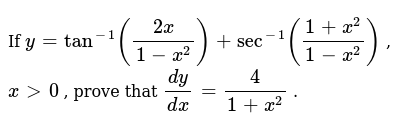



If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 X 0
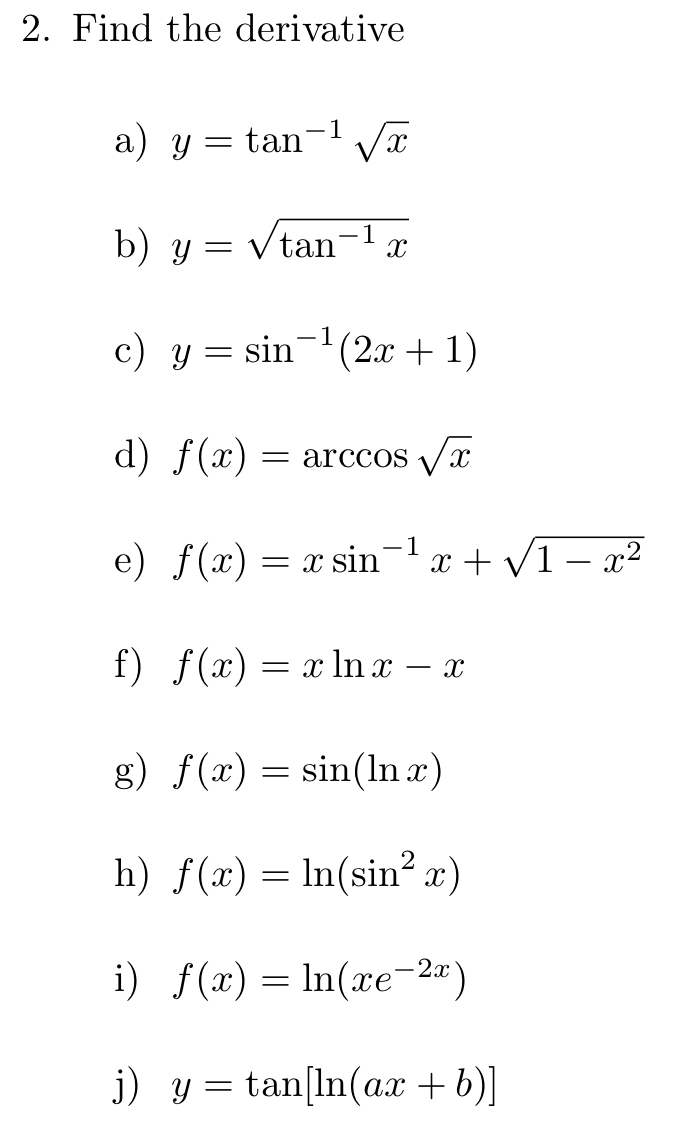



Solved 2 Find The Derivative A Y Tan 1 Vx B Y Vtan 1 A Chegg Com




How To Solve Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Cot 1 1 X2 2x Pie 3 Brainly In
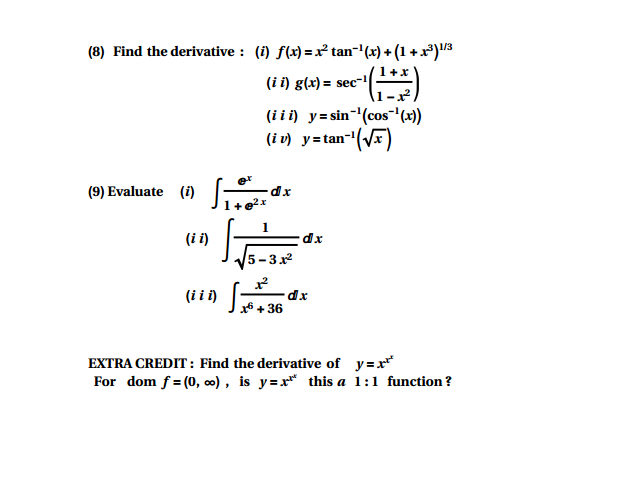



Solved Find The Derivative I F X X 2 Tan 1 X 1 Chegg Com




Ex 2 2 15 If Tan 1 X 1 X 2 Tan 1 X
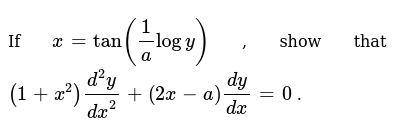



If X Tan 1 Alogy Show That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 2x A Dy




If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Find Dy Dx Class 12 Maths Doubtnut Youtube




Misc 44 Mcq Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is



Prove The Following Tan 1x Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Tan 1 3x X 3 1 3x 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Tan 1 Left Frac 3 X Sqrt X 1 3 X Right Then




Q31 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Then Show That X 2 1 2 D 2 Y Dx 2 2x X 2 1 Dy Dx 2 Youtube
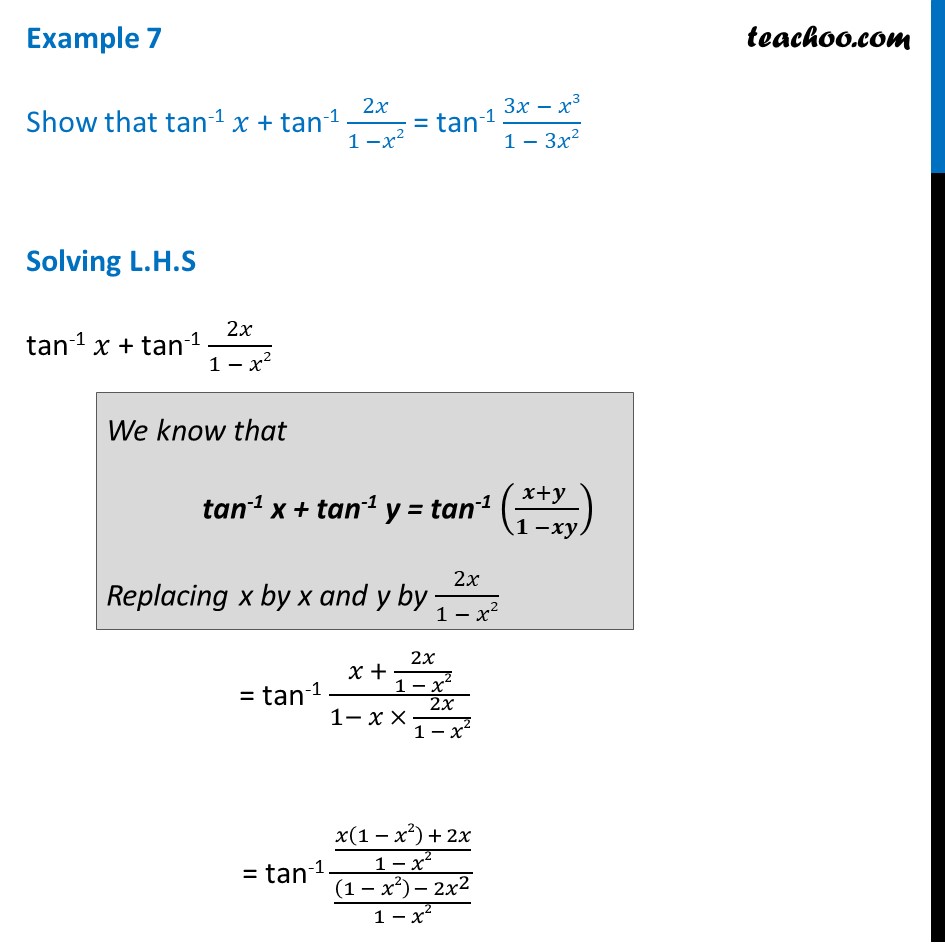



Example 7 Show That Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Inverse
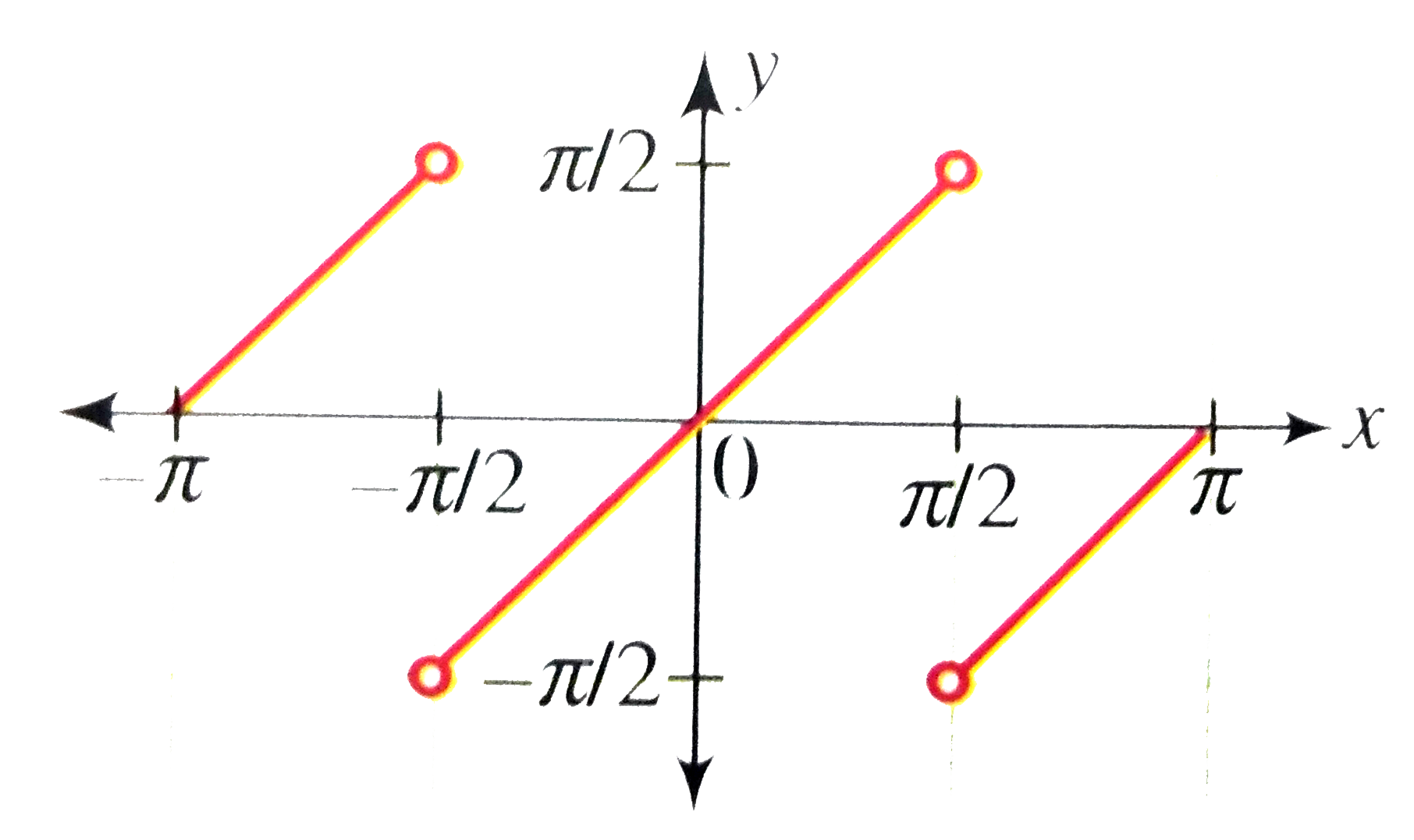



Draw The Graph Of Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2
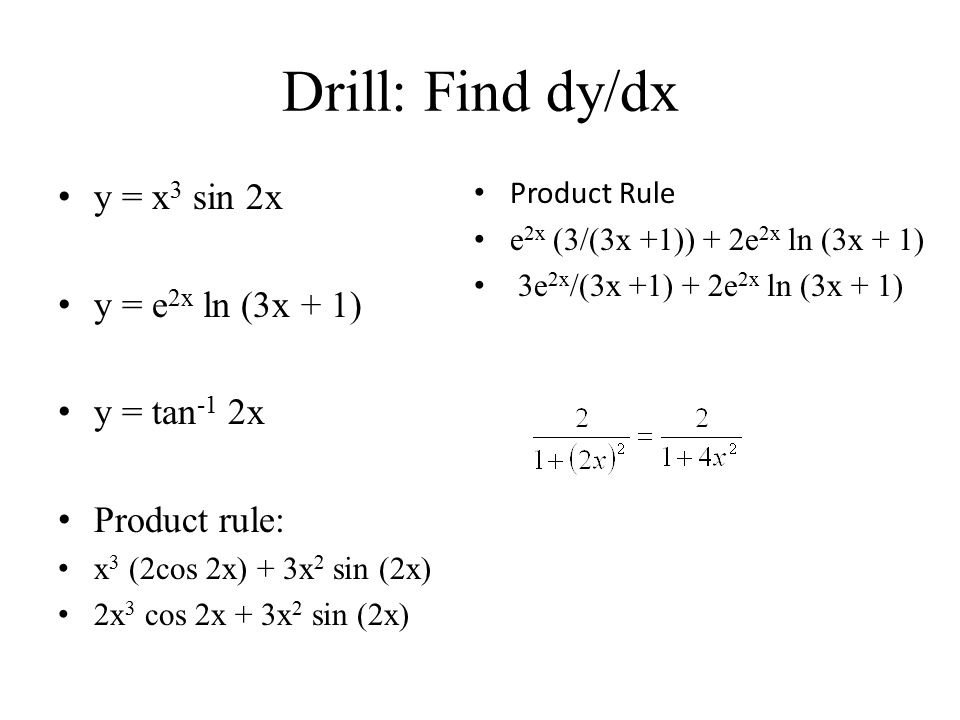



Drill Find Dy Dx Y X 3 Sin 2x Y E 2x Ln 3x 1 Y Tan 1 2x Product Rule X 3 2cos 2x 3x 2 Sin




If Y Tan 1 A X 1 Ax Then Dydx




If Y Tan 1 2x1 X 2 Tan 1 3x X 31 3x 2 Tan 1 4x 4x 31 6x 2 X 4 Then Show That Dydx 11 X 2




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1
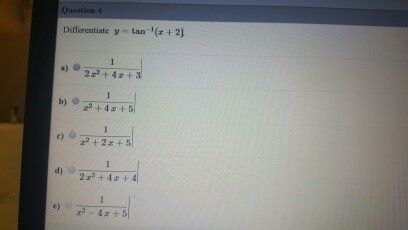



Solved Differentiate Y Tan 1 X 2 A 1 2x 2 4x 3 Chegg Com



How Do You Graph Y Tan 1 2 X Socratic



Solve For X Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Cot 1 1 X 2 2x P 3 1 X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Prove That Tan 1 1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X2 Cos 1 1 Y2 1 Y2 X Y 1 Xy If Ixi 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com




Solved 1 Find The Derivative Of The Following Functions A Chegg Com



If Y 2 Tan 1 X Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 For All X Then Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved 13 The Derivative Of Y Tan X Is Ed 1 X Out Of Chegg Com




Y Tan 1 2x 1 15 X 2 F I N D Dy Dx




If Y Tan 1 X 1 3 A 1 3 1 X 1 3 A 1 3 Then Find Dy Dx Youtube
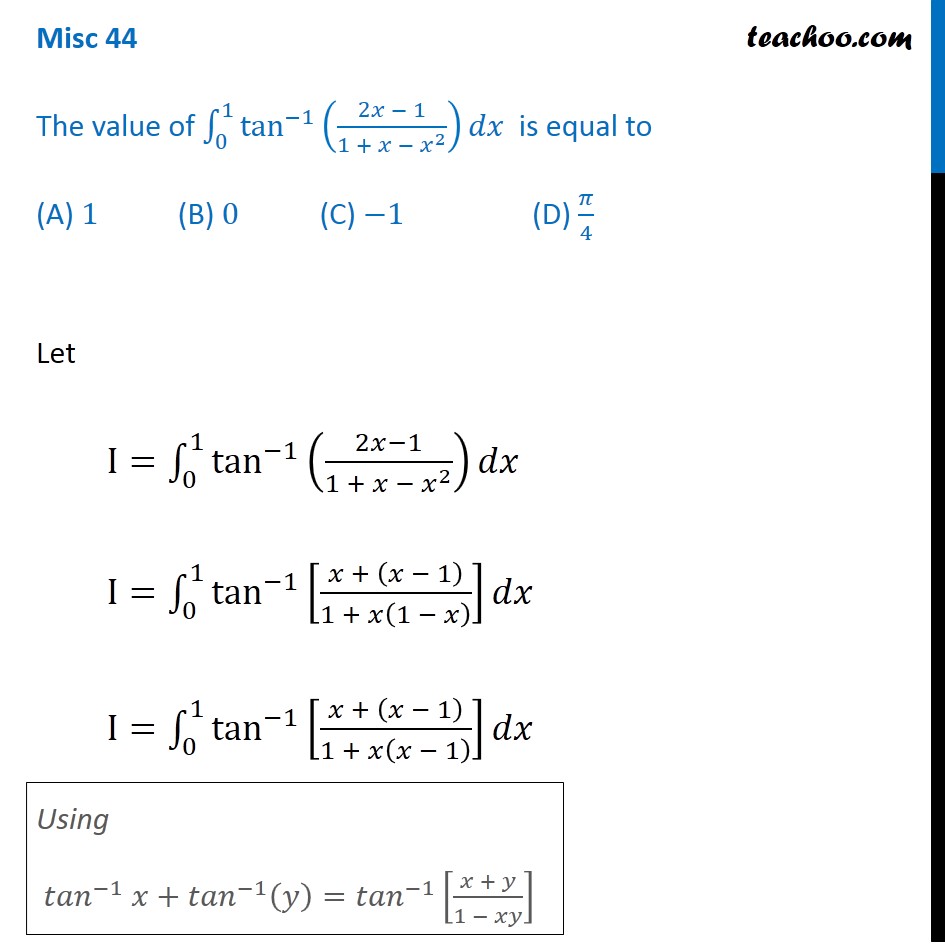



Misc 44 Mcq Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is
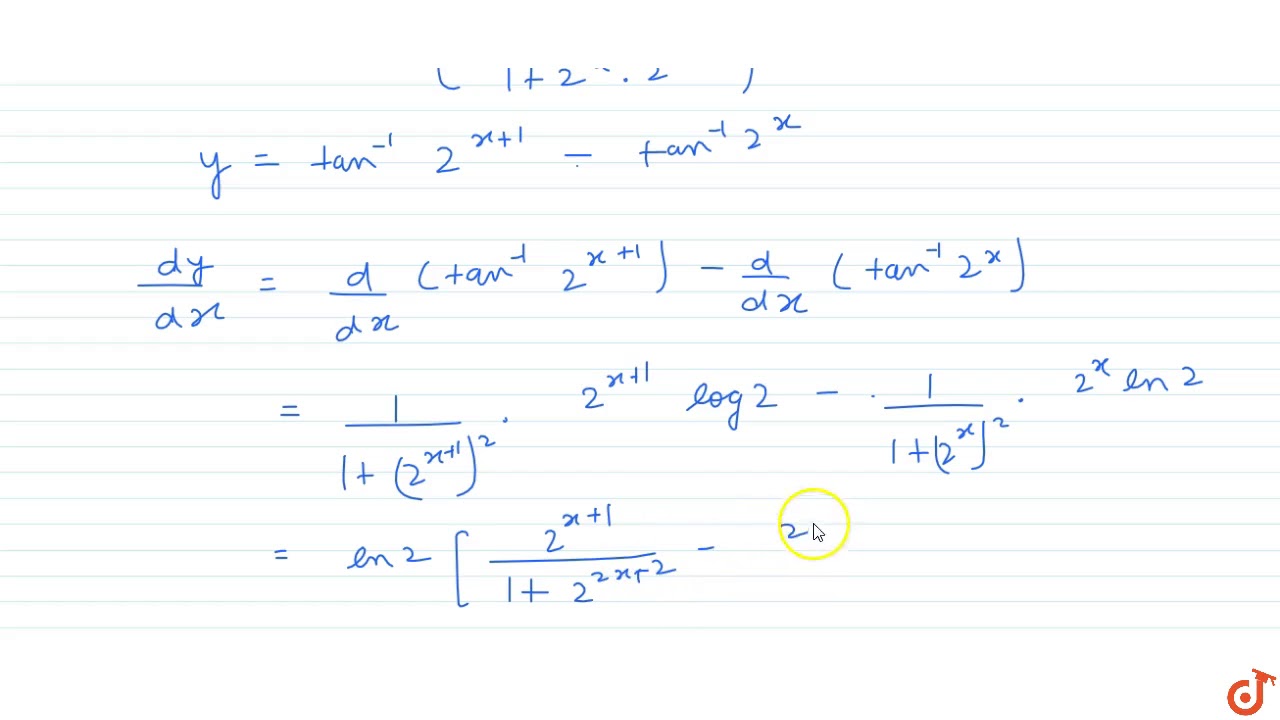



If Y Tan 1 2 X 1 2 2x 1 T H E N Dy Dx A Tx 0 Is 1 B 2 C 1n 2 D None Of T Youtube



If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 X 0 Prove That Dy Dx 4 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



How To Differentiate Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 For The Inverse Trigonometric Function Quora
コメント
コメントを投稿